Pipeline
Pipeline Status in NEORNAT
| Code name | Target validation | Proof of concept | In vivo efficacy | Non Clinical | IND Approval | Phase 1 | Indication | Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRT-YHD_001 | 2025’ 2Q | 2025’ 3Q | HCC | Macrophage immune-check point inhibitor | ||||
| NRT-YHD_002 | Lung cancer |
Macrophage immune-check point inhibitor | ||||||
| NRT-YHD_003 | Pancreatic cancer | Macrophage immune-check point inhibitor | ||||||
| NRT-KSY_001 | HCC | Competing endogenous RNA inhibitor | ||||||
| NRT-NMJ_001 | HCC | DNA mismatch repair enzyme inhibitor | ||||||
| NRT-NMJ_002 | Solid cancer |
DNA mismatch repair enzyme inhibitor | ||||||
| NRT-RD_MCMD | Early diagnosis of HCC | HCC |
NRT-YHD
Macrophage immune-check point inhibitor
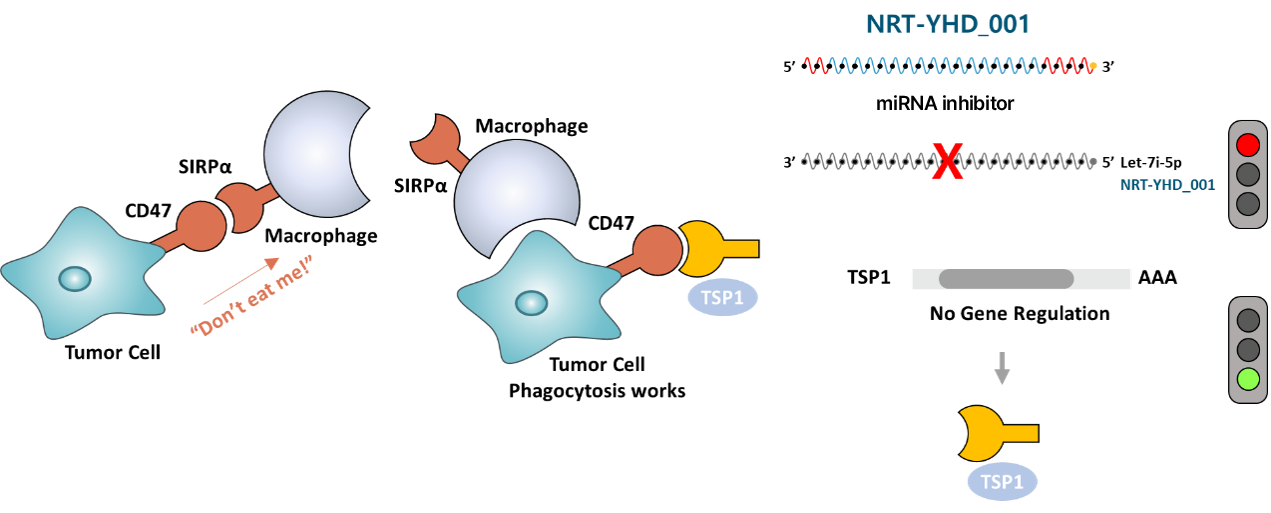
The let-7i-5p suppresses host macrophage immune surveillance by inducing the CD47-SIRPα-mediated “don’t eat me” signal. Based on new concept of macrophage immune regulatory mechanism, we are developing a first-in class RNA immunotherapy that activates macrophages by recovering potent endogenous tumor suppressor TSP1 via specific inhibiting let-7i-5p miRNAs in liver cancer cells.
NRT-YHD specifically inhibits let-7i-5p miRNA, which suppresses macrophage immunity (Don't eat me signal) during hepatocellular carcinogenesis, thereby allowing macrophages to elicit phagocytosis (Eat me signal) against liver cancer cells. In the development of liver cancer, oncomiR let-7i-5p suppresses translation of the THBS1 gene, thereby interfering in the governance of therombospondin-1 (TSP1) in the growth, proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis of liver cancer. This activation of macrophages is also expected to become an anticancer drug that can fundamentally remove cancer cells by activating the adaptive immune cells such as T-cells in tumor microenvironment.
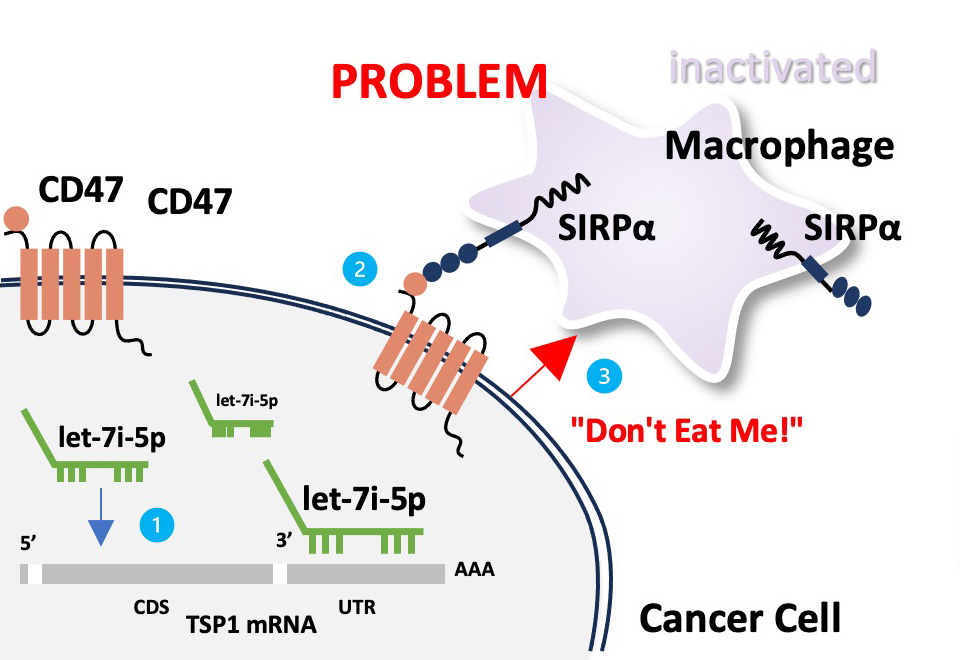
1) let-7i-5p miRNA suppresses translation of TSP1 mRNA, which leads to 2) the recognition of CD47 by SIRPα, activating the 3) "Don't Eat Me" signal of cancer cells.
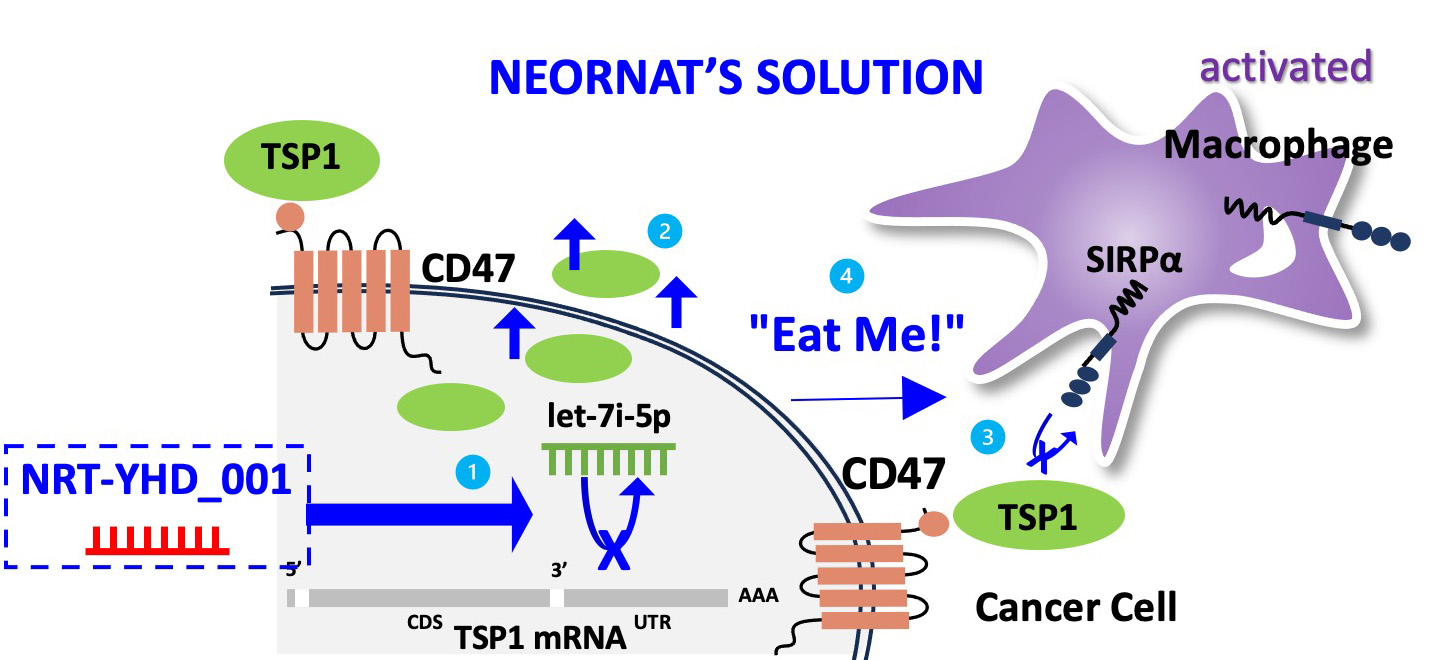
1) NEORNAT's 'NRT-YHD_001', an antisense miRNA for let-7i-5p, 2) restores translation of TSP1 which 3) inhibits interactions between CD47 and SIRPα. This 4) activates "Eat Me" signal for macrophage to eliminate cancer cells.
1. NRT-YHD_001 : RNA agent for Liver cancer with treatment RNA preparation with anticancer action of NRT-YHD mechanism
NRT-YHD_001 is an RNA liver cancer treatment pipeline with the mechanism of NRT-YHD. It restores the production of TSP1 in liver cancer tissue, binds TSP1 to CD47 of cancer cells, and activates macrophages to treat liver cancer. NRT-YHD-001 is an RNA liver cancer treatment pipeline with the mechanism of NRT-YHD. It restores the production of TSP1 in liver cancer tissue, binds TSP1 to CD47 of cancer cells, and activates macrophages to treat liver cancer. It is a drug that solves the problems of stability and tissue selectivity, which are problems with antisense RNA therapeutics, and has a high anticancer effect on liver cancer.
Efficacy & Key Data
In vivo Therapeutic Efficacy Test, Weekly Injection
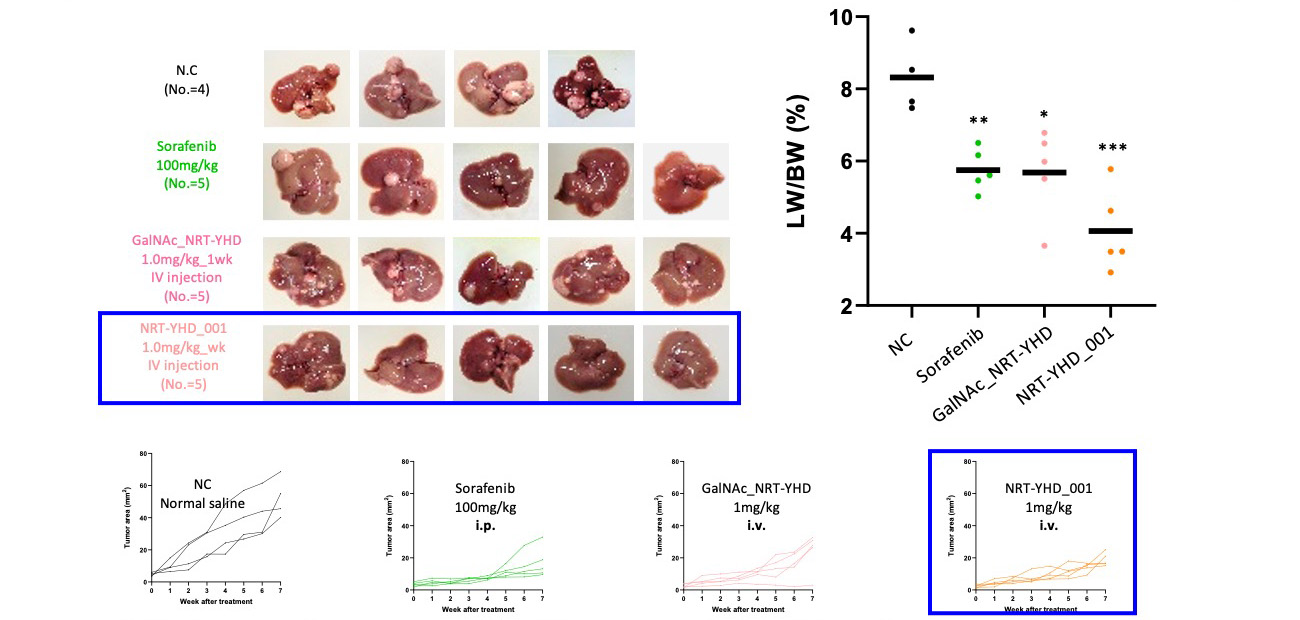
Highest decrease in liver weight/ body weight ratio
In vivo Therapeutic Efficacy Test, Biweekly Injection
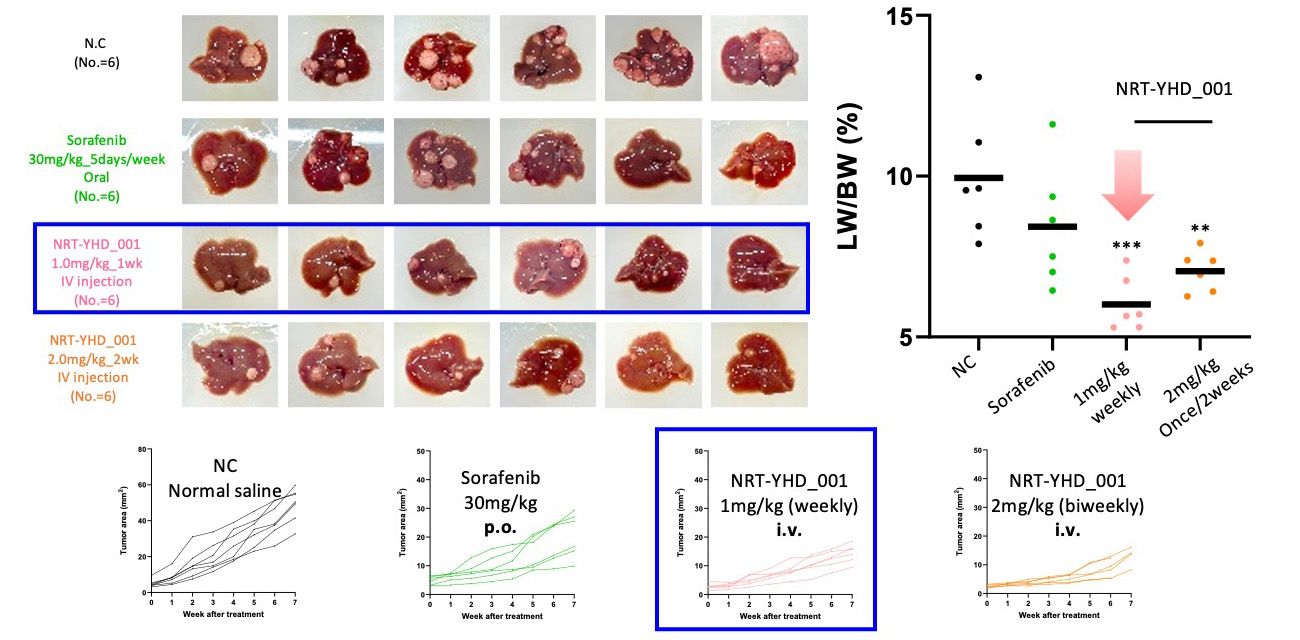
Highest decrease in tumor area
Therapeutic Efficacy Xenograft model survival Test
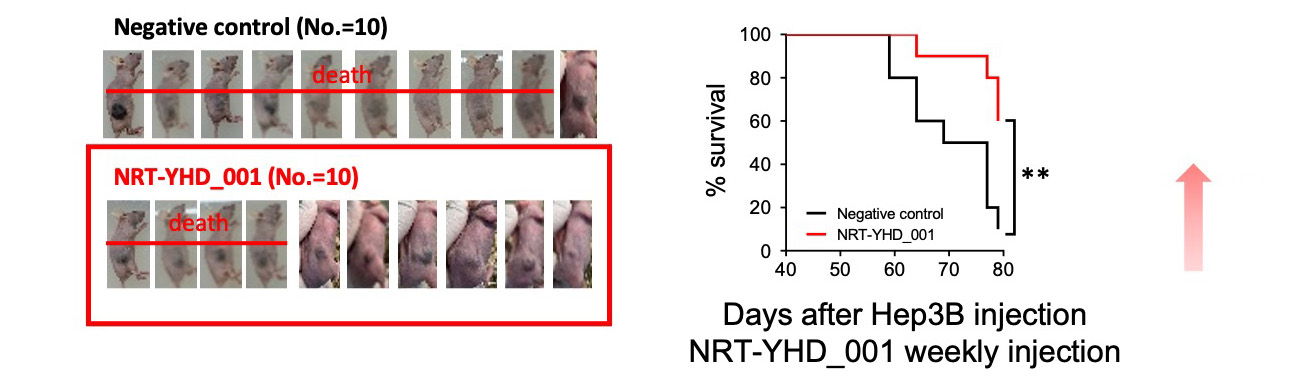
50% increase in survival rate compared to the negative control
Indication & Competitiveness
-
- BCLC B:
- intermediate stage
- BCLC C:
- advanced stage
Target patients : BCLC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer) B and C - patients who cannot receive surgery or have experienced a recurrence of liver cancer after receiving conventional treatments. -
NRT-YHD 001 is the one and only microphage immune-check point inhibitor in liver cancer therapeutics
-
It is anticipated to have significant synergy with combination therapies based on its mechanism of action.
-
Excellent safety profile in preliminary toxicity studies
Unmet Medical Needs
- Poor prognosis : The 5-year relative survival rate is less than 40%, indicating a very poor prognosis.
- Advancements with first-line immunotherapy : The approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors as a first-line therapy has significantly improved efficacy. However, challenges persist with an objective response rate of 30% and diminished effectiveness in patients with PD-L1 expression below 1% or those without a history of viral hepatitis.
- Limitations of immunotherapy : Notably, there is a lower response rate in patients with PD-L1 expression below 1% or those without a history of viral hepatitis, highlighting a challenge in achieving effectiveness with immunotherapy in certain patient subgroups.
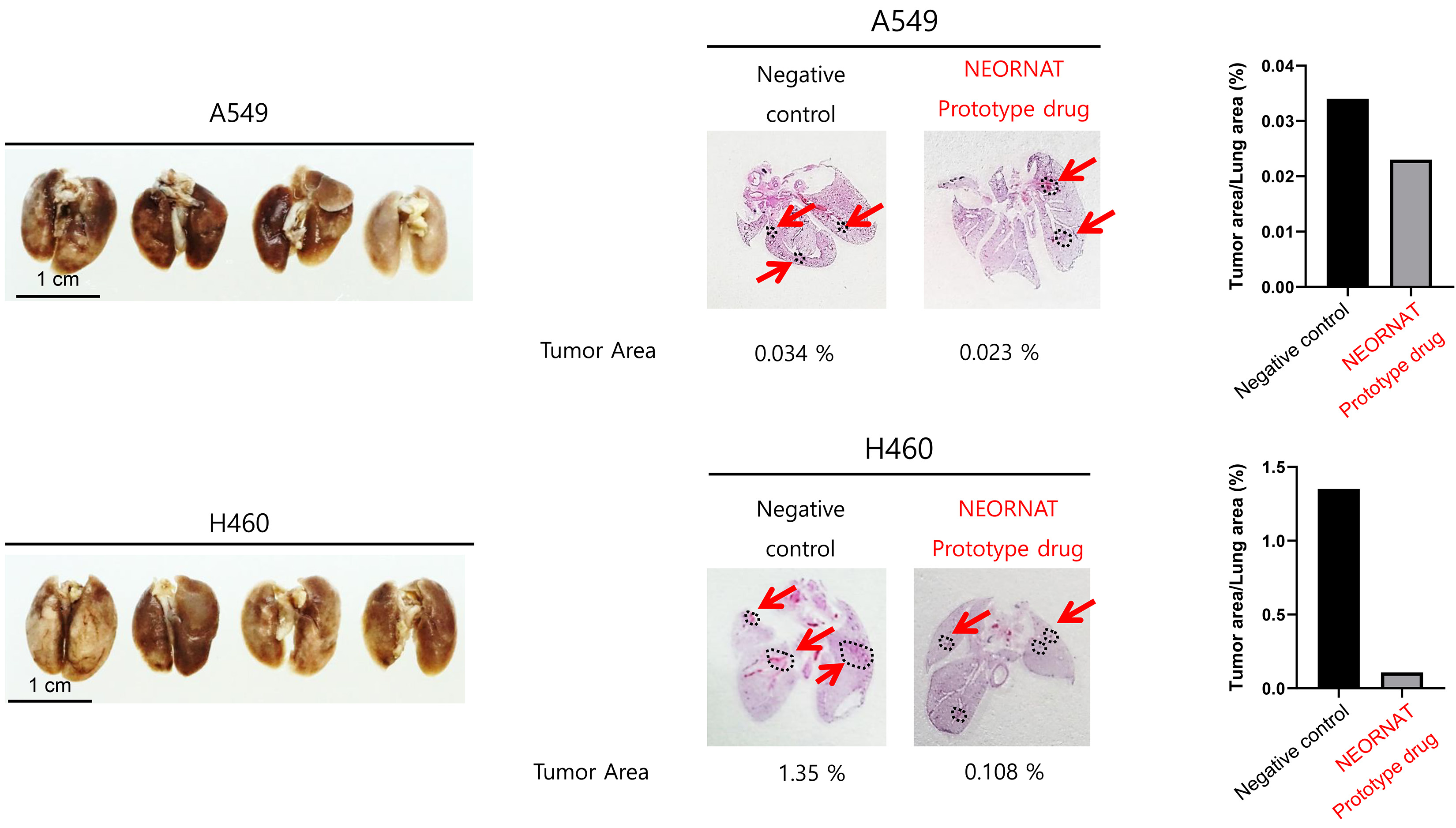
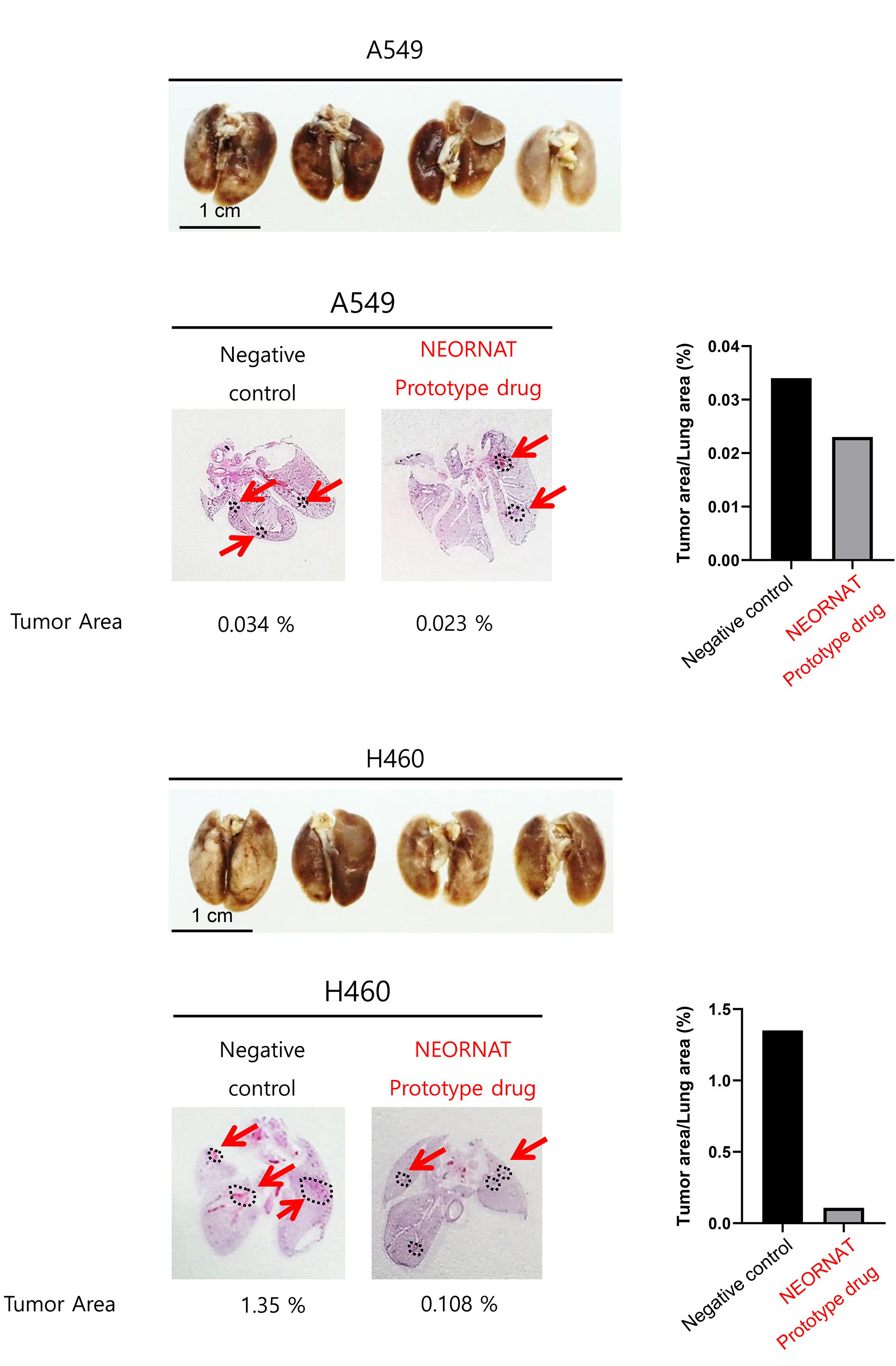
2. NRT-YHD_002 : RNA agent for Lung cancer with RNA preparation with anticancer activity of NRT-YHD
NRT-YHD_002 is an RNA lung cancer treatment pipeline with the mechanism of NRT-YHD, confirmed to be useful in lung cancer by big data analysis. NRT-YHD_002 confirmed in a human lung cancer cell line for increased TSP1 and activates macrophages and growth inhibition. in vivo validation, we plan to develop the first macrophage immune checkpoint inhibitor an anticancer drug for lung cancer.
NRT-KSY
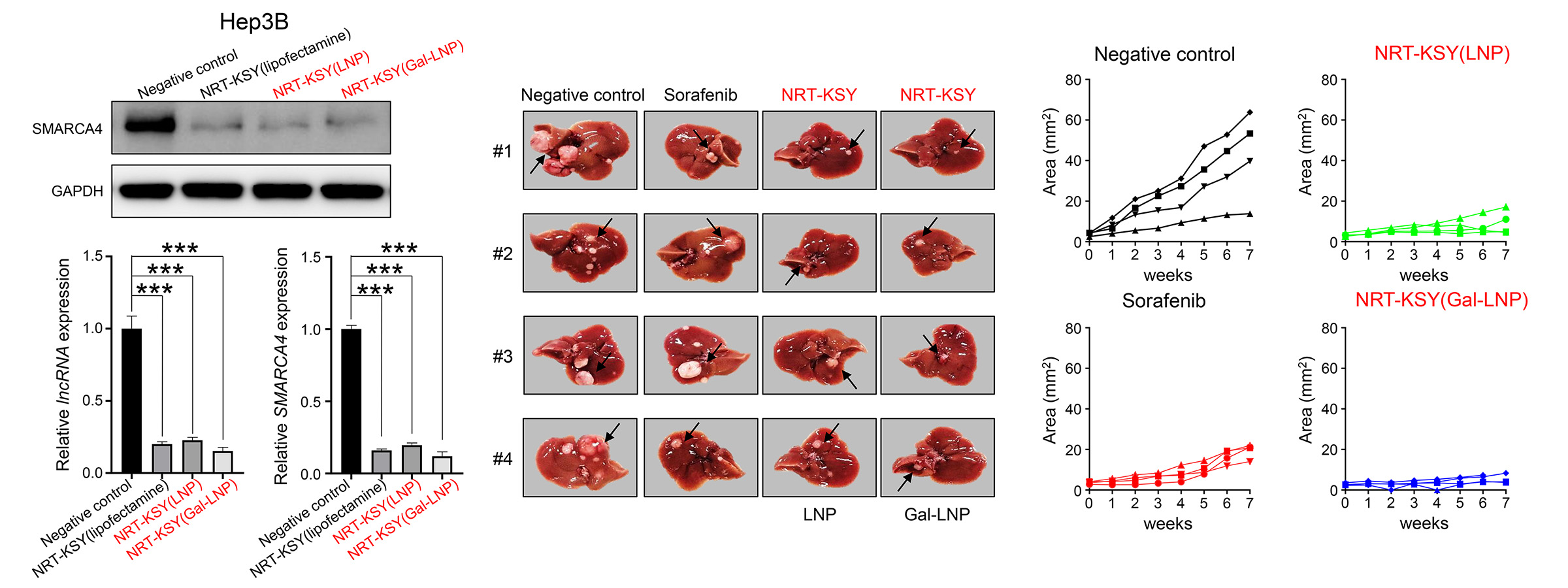
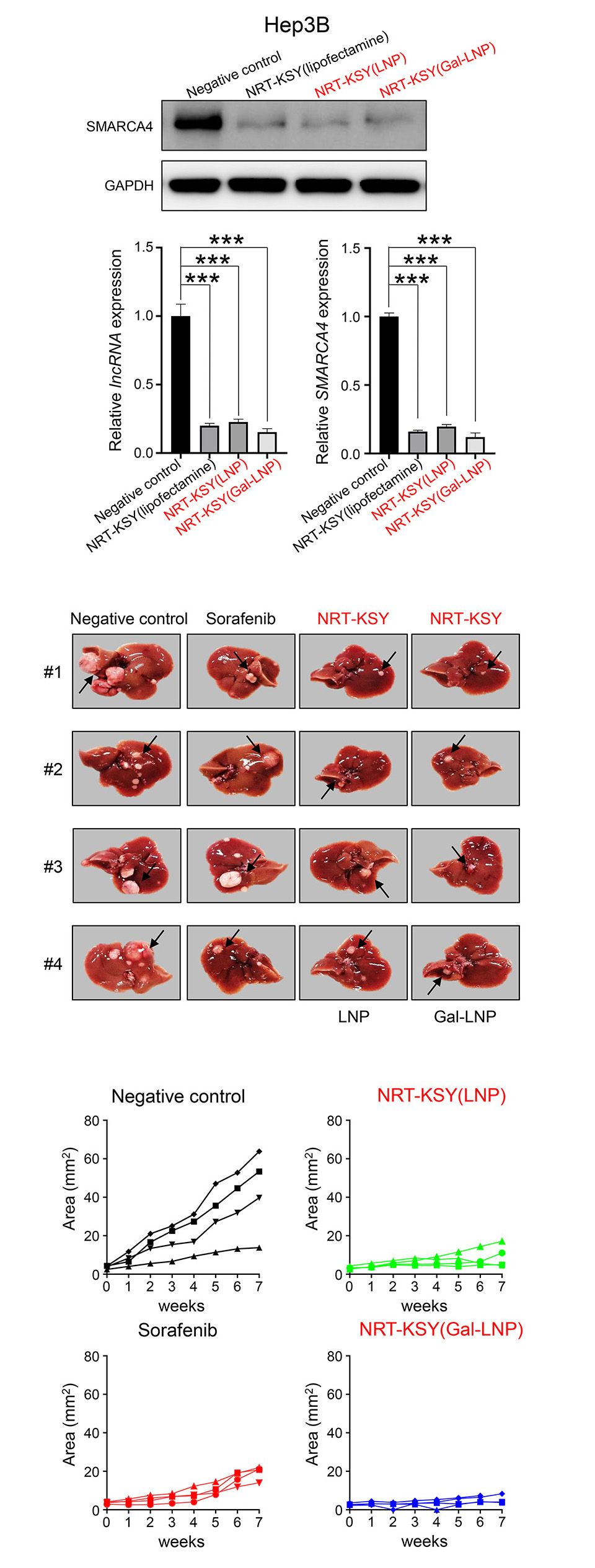
siRNA mix targeting oncogenic super enhancer RNA and long non-coding RNA
In liver cancer, SMARCA4 binds to the enhancer region of the oncogene IRAK1 and promotes the transcription of IRAK1, thereby promoting malignant liver cancer. On the other hand, we also found that certain specific long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) regulate SMARCA4 expression by sponging miRNA agaist SMARCA4 in liver cancer. Based on this mechanisms, we developed NRT-KSY which is a combination mixture of siRNAs simultaneously blocking the expression of SMARCA4 and lncRNA, which functions as sponging miRNA targeting SMARCA4. This NRT-KSY strongly suppresses both oncogenic super enhancer and SMARCA4 by two different siRNAs in liver cancer cells, and thereby effectively inhibits the formation and growth of liver cancer.
NRT-NMJ
DNA mismatch repair enzyme inhibitor
The NRT-NMJ targets a specific DNA replication enzyme. Recently, we found that a certain DNA replication enzyme was increased in most solid tumors by analysis of large cohort genomic datasets. NEORNAT inc., has verified that this enzyme plays a pivotal role in the development of cancer. Therefore, blocking this enzyme suppressed the expression of DNA methyltransferases, resulting in there-expression of tumor suppressor genes in cancer cells.
NRT-NMJ is a pipeline that increases the transcription of tumor suppressor genes by inhibiting the expression of this DNA methyltransferases with siRNAs that target specific DNA replication enzyme.
NRT-RD_MCMD
Liver Cancer Early Diagnosis Kit
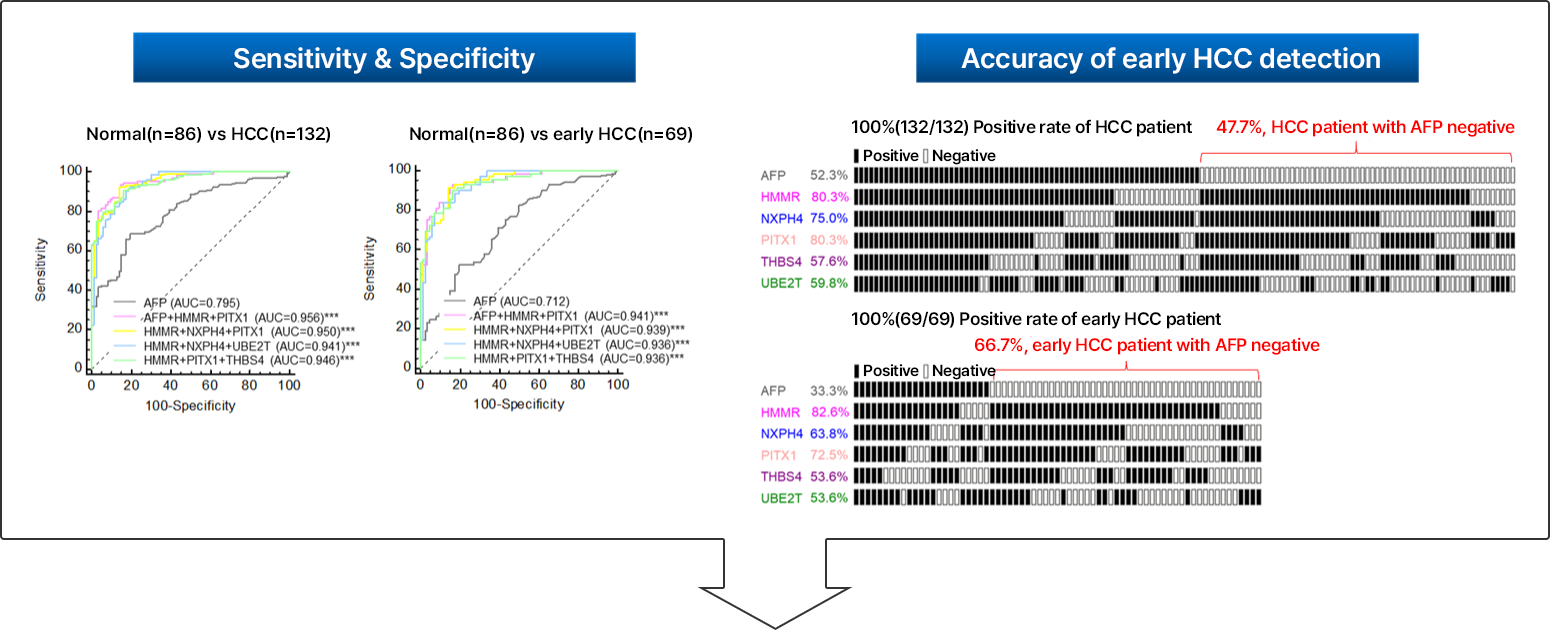
Early diagnosis of liver cancer is a very important factor in the patient's prognosis. Therefore, if diagnosed at an early stage, most liver cancer is curable. Early diagnosis of liver cancer is very important. Currently, most in vitro diagnostic devices related to cancer diagnosis use a method of confirming the presence or absence of a specific cancer by identifying specific biomarkers in the patient's blood. However, most of the developed cancer diagnostic kits are diagnostics for the purpose of detecting one specific marker and have low accuracy and sensitivity. In order to diagnose early liver cancer, we have developed an in vitro diagnostic device in the form of a panel kit that simultaneously measures and diagnoses multiple liver cancer markers with high specificity, and this technology is transferred to KPS Inc. in 2021 and is under development for commercialization.
Multiple HCC markers developed by NEORNAT Inc. have higher sensitivity and specificity than the existing single marker for liver cancer diagnosis. It can accurately diagnose early liver cancer.